In this post…
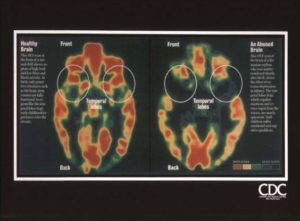
The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) Study is a groundbreaking research project that has transformed our understanding of how early-life trauma impacts long-term health. Conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Kaiser Permanente, the study revealed a strong correlation between childhood adversity and a wide array of mental and physical health issues in adulthood. This blog explores the ACEs Study, its implications for health, and how Mindfulness-Based Ecotherapy (MBE) can offer a pathway to healing.
What is the ACEs Study?
The ACEs Study evaluates the impact of adverse experiences during childhood, such as abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. Participants answer questions across ten categories:
- Physical abuse
- Emotional abuse
- Sexual abuse
- Physical neglect
- Emotional neglect
- Parental separation or divorce
- Household substance abuse
- Household mental illness
- Domestic violence
- Incarcerated household member
Each positive response counts as one ACE. Higher ACE scores correlate with increased risks of health challenges such as depression, anxiety, chronic diseases, and even early death.
ACEs Survey:
- Did a parent or other adult in your household often or very often… swear at you, insult you, put you down, or humiliate you? Or act in a way that made you afraid you might be physically hurt?
- Did a parent or other adult in your household often or very often… push, grab, slap, or throw something at you? Or ever hit you so hard that you had marks or were injured?
- Did an adult or person at least 5 years older than you ever… touch or fondle you in a sexual way? Or have you touch their body in a sexual way? Or attempt or actually have oral, anal, or vaginal intercourse with you?
- Did you often or very often feel that… no one in your family loved you or thought you were important or special? Or your family didn’t look out for each other, feel close to each other, or support each other?
- Did you often or very often feel that… you didn’t have enough to eat, had to wear dirty clothes, and had no one to protect you? Or your parents were too drunk or high to take care of you or take you to the doctor if you needed it?
- Were your parents ever separated or divorced?
- Was your mother or stepmother: Often or very often pushed, grabbed, slapped, or had something thrown at her? Or sometimes, often, or very often kicked, bitten, hit with a fist, or hit with something hard? Or ever repeatedly hit over at least a few minutes or threatened with a gun or knife?
- Did you live with anyone who was a problem drinker or alcoholic or who used street drugs?
- Was a household member depressed or mentally ill, or did a household member attempt suicide?
- Did a household member go to prison?

Impacts of ACEs on Health
The ACEs Study uncovered that individuals with higher ACE scores are at greater risk for the following:
- Mental Health Issues: Depression, anxiety, PTSD, and suicidal ideation are common among those with high ACE scores.
- Physical Health Problems: Chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders are more prevalent in those with childhood trauma.
- Behavioral Challenges: Increased likelihood of substance abuse, risky behaviors, and difficulty forming healthy relationships.
- Shortened Lifespan: Studies indicate a reduced life expectancy of up to 20 years for those with the highest ACE scores.
Healing Through Mindfulness-Based Ecotherapy
Mindfulness-Based Ecotherapy (MBE) is a therapeutic approach that combines mindfulness practices with nature-based activities. It is particularly effective for individuals recovering from childhood trauma and attachment disorders. Here’s how MBE can help:
1. Rebuilding Secure Attachments
ACEs often disrupt the ability to form secure relationships. MBE includes exercises like grounding and mindful observation in natural settings, fostering a sense of safety and connection. These practices encourage individuals to rebuild trust—both in themselves and in their environment.
2. Managing Stress and Anxiety
MBE techniques such as mindful breathing, walking meditations, and sensory awareness exercises help regulate the nervous system. These activities mitigate the hyperarousal and emotional dysregulation common in individuals with high ACE scores.
3. Fostering Resilience
By engaging in eco-art activities like sandtray therapy or nature journaling, participants can explore their trauma narratives in a non-threatening way. These creative outlets enable them to reframe their experiences, cultivating resilience and empowerment.
4. Improving Physical Health
Spending time in nature has been shown to lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and improve overall physical health. The incorporation of mindfulness enhances these benefits by reducing chronic stress, a key factor linking ACEs to poor health outcomes.
5. Encouraging Emotional Regulation
Nature-based mindfulness exercises encourage individuals to stay present and process emotions as they arise. Over time, these practices strengthen emotional regulation skills, reducing symptoms of PTSD and anxiety.
Conclusion
The ACEs Study has provided invaluable insights into how childhood adversity impacts health across the lifespan. While the effects of high ACE scores can be profound, healing is possible. Mindfulness-Based Ecotherapy offers a holistic approach to addressing trauma, fostering resilience, and improving both mental and physical health. By integrating mindfulness practices with the healing power of nature, MBE provides a pathway for individuals to reclaim their well-being and build a brighter future.
If you or someone you know has experienced childhood trauma, consider exploring Mindfulness-Based Ecotherapy as a powerful tool for healing and growth.
Share Your Thoughts on the Adverse Childhood Experiences Study!
Do you find the ACE Study useful? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Don’t forget to check out our YouTube Channel!